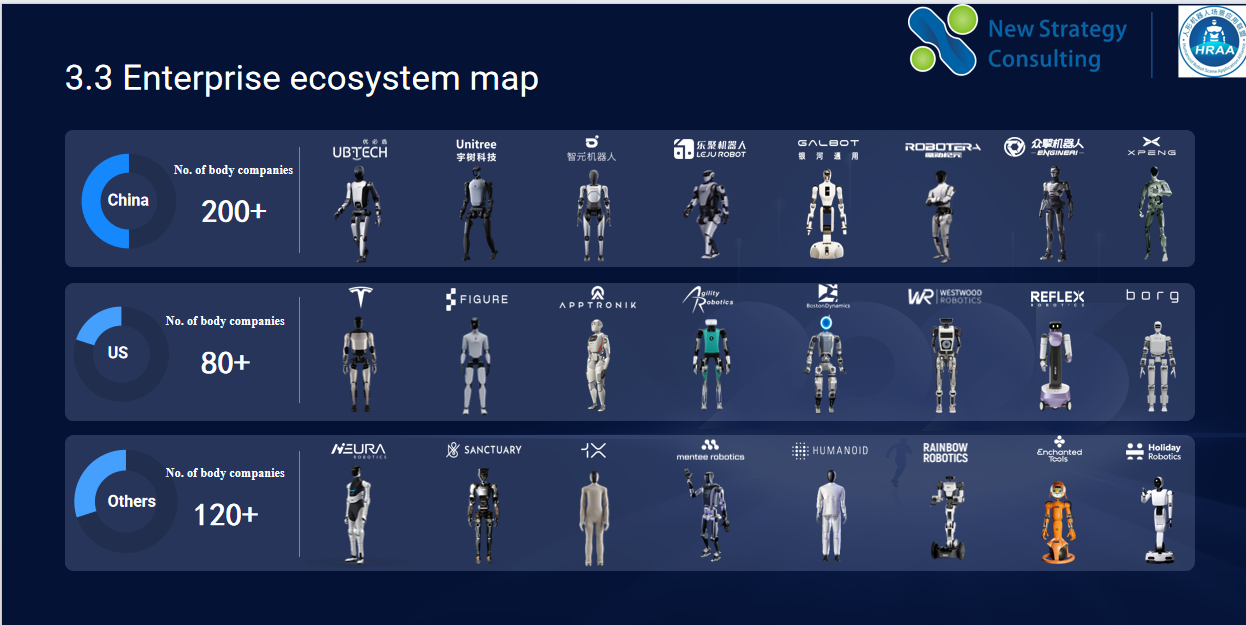
According to the latest statistics from China Mobile Robot Industry Alliance (CMRA) and Humanoid Robot Scene Application Alliance (HRAA), there are currently over 200 humanoid robot manufacturers in China.
Furthermore, the data only include companies that have released related products or showcased prototypes, representing a relatively conservative estimate; considering that many teams are still in the R&D phase and have not yet publicly announced their results, the actual number of entrants is likely much higher.
With 90 new entrants in just seven months, the industry is accelerating its expansion.
It’s worth noting that the humanoid robot industry is expanding at an unprecedented pace. In April of this year, there were only 110 registered humanoid robot manufacturers in China, but by November, this number had exceeded 200. In just seven months, the number of companies has almost doubled, demonstrating a strong industry absorption capacity and technology spillover effect.
At the same time, the pace of product iteration is also accelerating significantly. From January to October 2025, the industry has released over 137 new humanoid robot products, maintaining a pace of almost one new model every two to three days. This significant increase in new products reflects not only accelerated technological breakthroughs but also continuous capital investment in the embodied intelligence field, with substantial resources concentrating on leading companies and promising teams. (Further reading: Over 44 new humanoid robots hit the market in Q3 2025)
Overall, both the rapid expansion of the number of companies and the high density of new product releases indicate that the humanoid robot sector is undergoing a high-speed development phase driven by both technology and capital. The continued rise in industry activity also means that the competitive landscape will solidify more quickly, with technological barriers, supply chain capabilities, and commercialization paths becoming key watersheds in the next stage.
The industry exhibits a clear clustering effect, with first-tier cities dominating.
Currently, China’s humanoid robot industry landscape is characterized by regional clustering and high concentration.
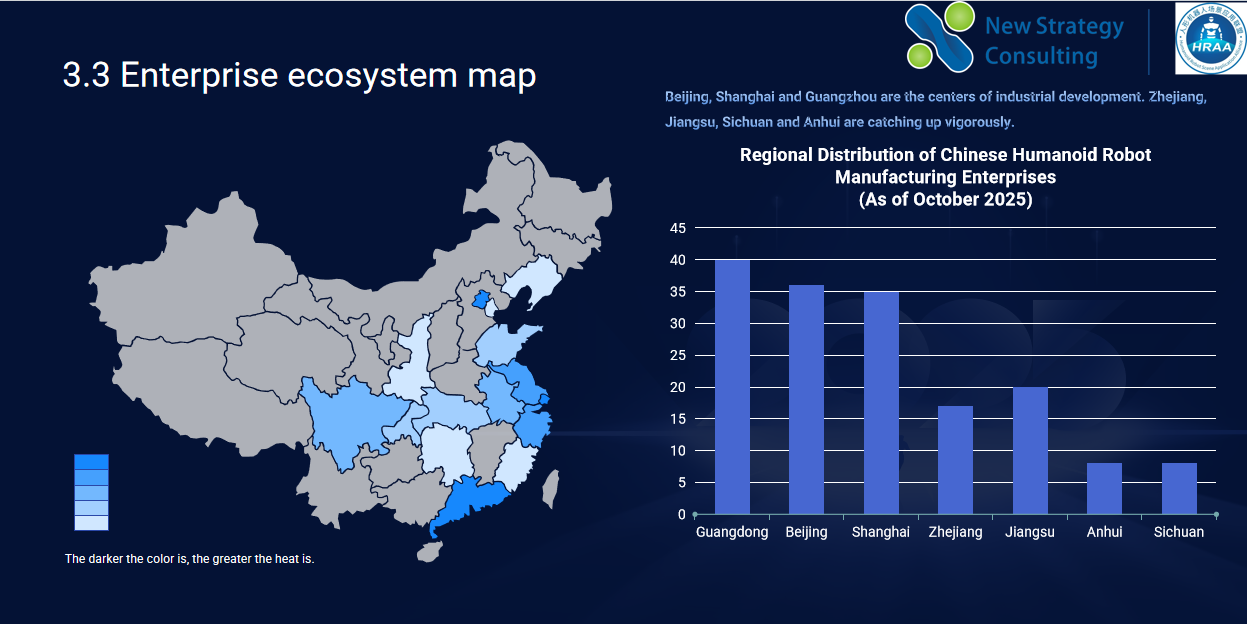
Guangdong, Beijing, and Shanghai constitute the three core industrial regions, forming a pattern of concentrated and interconnected enterprise development. Provinces such as Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Sichuan, Anhui, and Shandong have also quickly followed suit, introducing relevant support policies in an effort to seize the initiative in this new arena.
At the city level, Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen together account for 56% of the total number of humanoid robot companies nationwide, demonstrating extremely high industry concentration.
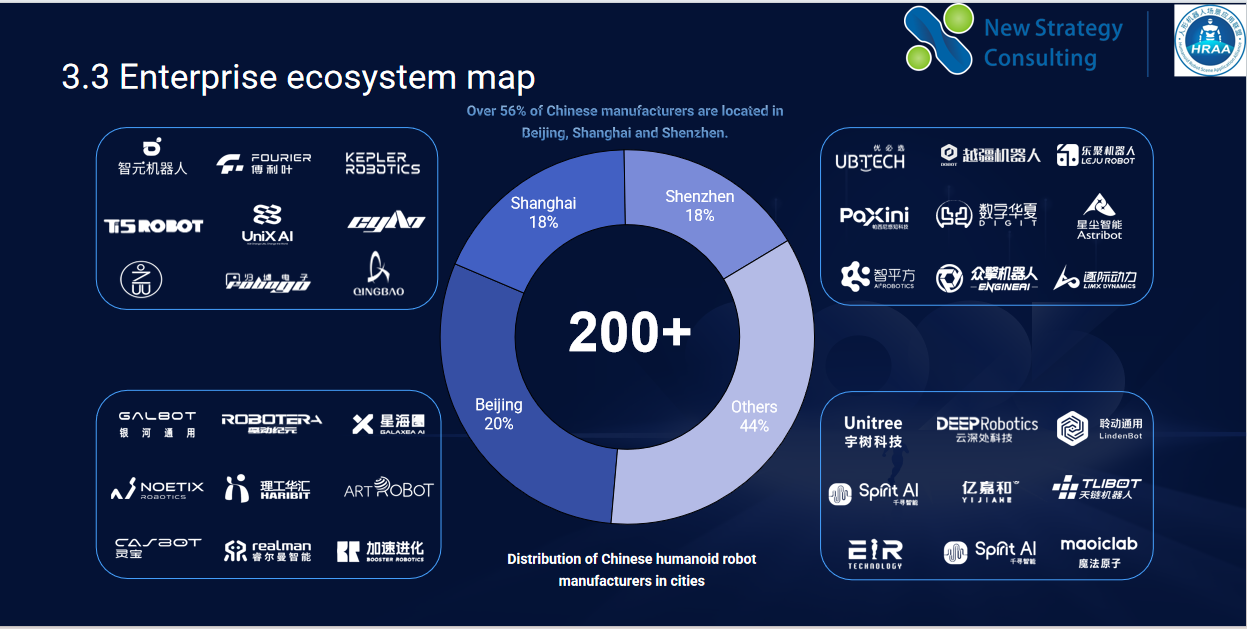
Beijing is home to representative companies such as Xiaomi Robotics, Robotera, Galbot, and Realman; Shanghai boasts strong players like AGiBOT, Fourier, and Kepler; and Shenzhen is a key base for companies such as UBTECH, Dobot, Leju Robot, EngineAI, DIGIT, and Paxini.
These three cities not only possess abundant industrial chain resources and talent supply but also a relatively complete research ecosystem, providing strong support for humanoid robot R&D.
Simultaneous emergence of startups and cross-industry players, and the increasing diversification of company types
The humanoid robot sector is showing a trend towards diversification and cross-industry integration amidst the continued global surge in popularity.
In terms of company attributes:
Startups established within the last five years account for 52%. These innovative teams are a vital force driving the rapid evolution of industry technology. Representative companies include AGiBOT, Limx Dynamics, Robotera, EngineAI, and X Square Robot.
Cross-industry companies account for 14%, with companies from home appliances, automobiles, and the internet sectors entering the market. Representative companies include Midea, Xiaomi, XPENG, and GAC Group, while giants like BYD and CATL have also reportedly been developing their own embodied intelligent robots.
Specialized robot companies account for 25%, with companies deeply rooted in the robotics field possessing strong advantages in technology, supply chain, and application scenarios. Representative companies include Unitree, Deep Robotics, KEENON, Pudu Robotics, and Dobot.
Robot component companies account for 9%, with the addition of upstream suppliers further improving the industry ecosystem. Representative companies include TLIBOT and Ti5robot.
With three parallel development paths, China’s humanoid robots are accelerating their three-dimensional development
As the number of companies rapidly expands, differences in technical routes and strategic directions among different companies are gradually becoming apparent. Currently, the industry can be broadly categorized into three typical paths:

The first one is “hardware-oriented”, represented by companies such as Unitree, EngineAI, and NOETIX. Their core advantage lies in their self-developed capabilities in underlying hardware. These companies have long been dedicated to key components such as servo drives, joint modules, lightweight structures, and power systems, attempting to build competitive barriers through continuous iteration of physical performance and cost optimization, relying on “hardcore engineering capabilities.”
The second one is “software-oriented”, such as Galbot and X Square Robot. They emphasize large-scale models, embodied intelligent algorithms, and behavioral control systems as core drivers, improving robots’ understanding and execution capabilities through breakthroughs in algorithms, data, and decision-making systems. In this school of thought, the evolution of general intelligent capabilities is the key to determining the future landscape of the industry.
The third one is “scenario-oriented (full-stack)”, represented by companies such as AGiBOT, UBTECH, and Robotera. These companies typically possess both complete machine design capabilities and deep expertise in typical application scenarios. Through self-developed practices across the entire value chain of “hardware + software + scenario,” they drive the early deployment of robots in manufacturing, logistics, and commercial services. Their advantage lies in their ability to quickly validate needs, accumulate data, and form scalable business models.
With the rapid expansion of the humanoid robot industry, these three approaches are collectively forming the backbone of China’s humanoid robot ecosystem, indicating that future competition will revolve around three main lines: breakthroughs in underlying technologies, evolution of intelligent algorithms, and the ability to commercialize scenarios.
Coexistence of “speed” and “bubble” and pace under the joint control of regulators and the industry
From the current situation, China humanoid robot industry is transitioning from a “technology exploration period” to a “rapid expansion period.” At the national level, “how to strike a balance between promoting innovation and preventing bubbles” has become an important issue.
On November 27, Li Chao, Deputy Director of the Policy Research Office of the National Development and Reform Commission, pointed out at a press conference that speed and bubbles are always a relationship that needs to be carefully managed in the development of cutting-edge industries, and the humanoid robot industry is no exception.
He emphasized that humanoid robots are still immature in terms of technology, business models, and application scenarios, while the rapid influx of capital has led to over 150 related companies in China, more than half of which are startups or cross-industry teams. While this helps stimulate innovation, it also presents potential risks such as severe product homogenization, wasted resources due to redundant R&D, and squeezed R&D space.
Therefore, how to build differentiated competition, promote technological breakthroughs, and avoid blindly following trends will be crucial for the industry in the coming period.
The next 3-5 years will be a critical period for the industry to shift from “quantitative growth” to “quality improvement,” from “demonstration prototypes” to “mass production,” and from “technology competition” to “application scenario implementation.”
For each company, what’s more important than simply “entering the market” is the ability to build genuine core competitiveness, weather industry fluctuations, and achieve long-term value.

On December 5, the 3rd Ecological Conference for Embodied Intelligence Humanoid Robot Scenario Application 2025 will be held at Hefei Platinum Hanjue Hotel. This conference focuses on scenario applications and aims to explore in-depth development paths for technological innovation and application implementation. Stay tuned!



探索者论坛-scaled.jpg)
