According to statistics from China Humanoid Robot Scene Application Alliance (HRAA), as of January 2026, there were over 30 unicorns (valued at over $1 billion and less than ten years old) in this field globally, with over 13 of them exceeding 10 billion yuan in valuation.
This article will focus on the development of representative Chinese companies. (Further reading: https://cnmra.com/latest-progress-of-six-american-humanoid-robot-unicorns-valued-at-over-10-billion-in-2025/)
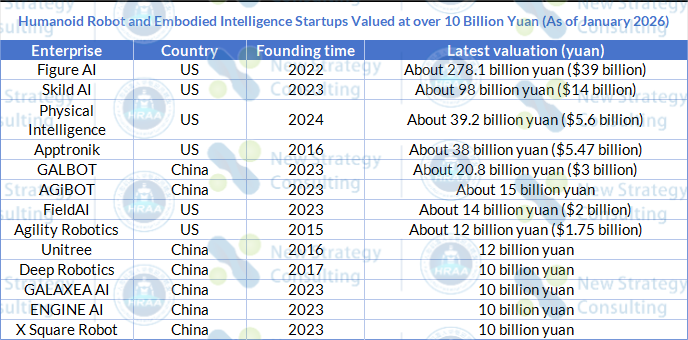
(Based on publicly available information on the Internet. If there are any incomplete parts, please make a correction.)
GALBOT
In 2025, GALBOT transitioned from a startup focused on embodied intelligence to one of the few domestic players achieving a valuation of 10 billion yuan and securing large-scale orders.
At the beginning of the year, GALBOT began promoting the deployment of embodied intelligent robots in actual commercial scenarios. In February, MIRACLE AUTOMATION and GALBOT signed an agreement to establish a joint venture, integrating their respective advantages and resources to conduct strategic cooperation on large-scale applications of embodied intelligent models and robots in the automotive manufacturing industry.
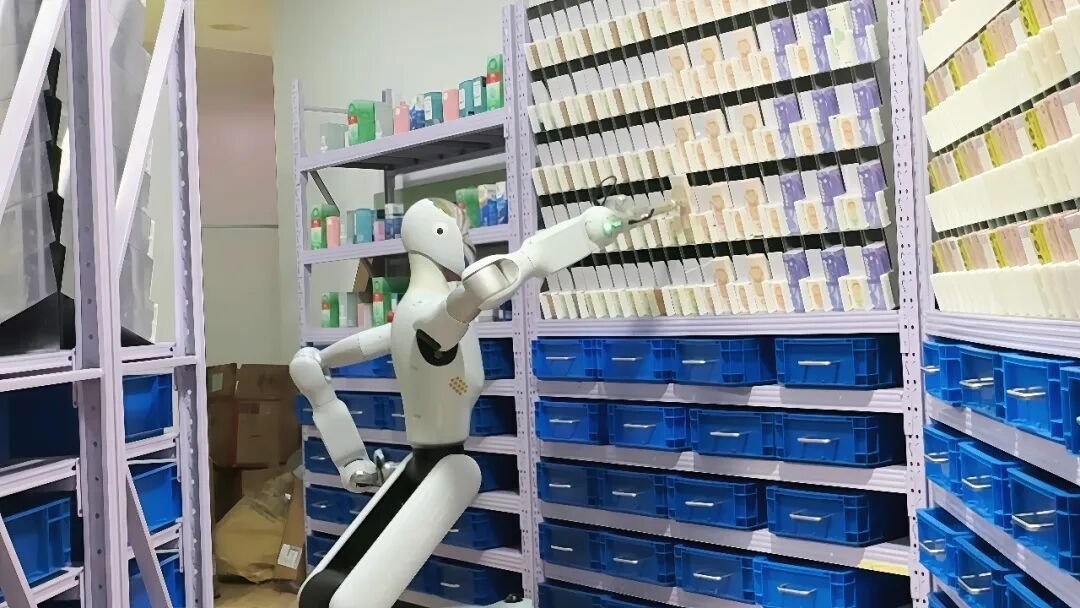
In March, GALBOT officially released the world’s first humanoid robot smart retail solution, which entered routine operation in nearly 10 stores in Beijing, used to complete basic tasks such as merchandise retrieval and display organization, accumulating real-world operational data for subsequent model optimization and large-scale replication.

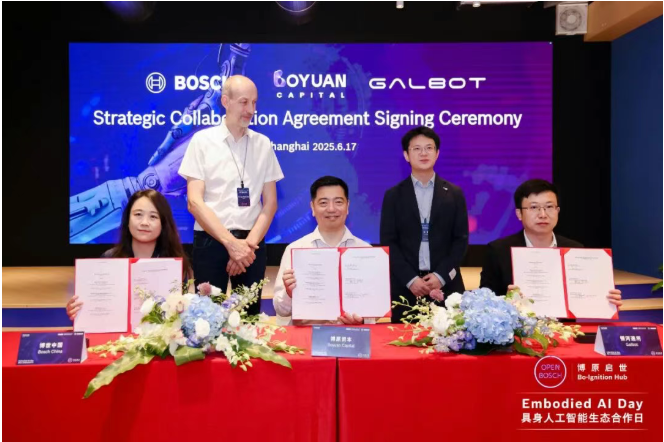
In June, GALBOT announced a joint venture with Bosch Group’s Boyuan Capital to promote the commercialization of humanoid intelligent robots in industrial manufacturing scenarios. Its robot platform began to perform real physical tasks in industrial environments such as automotive manufacturing, verifying its collaborative capabilities and on-site stability in complex processes.

Simultaneously, the company reached a key financing milestone. GALBOT completed a new round of financing led by CATL, raising approximately 1.1 billion yuan in a single round, bringing its total financing amount in two years to over 2.4 billion yuan. With this round of financing, the company’s valuation exceeded $1 billion, entering the unicorn category.
In terms of products and technology, GALBOT gradually clarified its product and model system by 2025. The company released multiple end-to-end embodied intelligence models, including GraspVLA for grasping and manipulation, GroceryVLA for retail scenarios, and TrackVLA for dynamic target tracking, which were used to support continuous task execution by robots in retail and industrial settings.
In the second half of the year, GALBOT’s capital process accelerated further. In December, the company completed a new round of financing exceeding $300 million, raising its overall valuation to the $3 billion level, making it one of the highest-valued embodied intelligence companies in China. Official disclosures indicate that this round of financing will primarily be used to expand product delivery capabilities, accelerate deployment in industrial scenarios, and advance preparations for large-scale production.
Following the financing, GALBOT gave a clearer signal on the order side. In the same month, the company announced a strategic cooperation agreement with precision manufacturing company Baida, planning to deploy more than 1,000 embodied intelligent robots within its manufacturing system and open its complete production line as a long-term verification scenario. This order of over 1,000 units represented a rare large-scale commercial cooperation case in the domestic embodied intelligence field by 2025.
AGiBOT
In 2025, AGiBOT shifted its development focus from single-technology and product advancement to a comprehensive transformation centered on mass production, capital operations, and ecosystem building around humanoid robots. In this year, the company made significant strides in product scale, industry control, and business model exploration, becoming one of the most active companies in China’s humanoid robot sector.
At the beginning of the year, AGiBOT officially clarified its humanoid robot mass production roadmap, simultaneously disclosing that its cumulative shipments had reached several thousand units. The company’s product system gradually became clearer, focusing on general-purpose humanoid robot bodies plus scenario-specific versions, emphasizing engineering indicators such as “mass production, delivery, and maintainability.”
Entering the first half of the year, AGiBOT simultaneously advanced key actions at both the capital and industry levels. The company completed its Series B financing, increasing its post-investment valuation to approximately 15 billion yuan. This round of financing will primarily be used to expand the size of its R&D and engineering teams and support the simultaneous advancement of product mass production and scenario deployment. At the same time, AGiBOT accelerated its ecosystem development, continuously extending into the upstream and downstream of the industry chain through direct and joint investments.
In July, AGiBOT took a key step in its capital operations. Through related entities, the company announced its intention to acquire control of SW Ancor through a combination of negotiated transfer and tender offer, resulting in a 63% stake. This move is seen as a significant milestone in its expansion into the manufacturing and materials sectors, marking its strengthening of control over key industrial resources through mergers and acquisitions.
In August, AGiBOT completed a strategic financing round, introducing international industrial and financial capital such as LG Electronics and Mirae Asset. While the amount raised was not disclosed, it was widely regarded as a significant endorsement of AGiBOT’s international capital base, further expanding its industrial and global cooperation space.
In terms of ecosystem building, AGiBOT’s activities in 2025 were particularly intensive. Public information shows that since 2024, the company has invested in and incubated more than 36 companies, directly or jointly. These investments cover core areas such as robot manufacturers, large models, key components, and application scenario development. Simultaneously, AGiBOT has established at least 17 joint ventures with several listed companies, local state-owned enterprises, and leading investment institutions.
Furthermore, over 40 listed companies have established multi-dimensional partnerships with AGiBOT, encompassing investment and ecosystem collaboration. These partners cover various aspects of the industry chain, such as component supply, high-end manufacturing, and channel and scenario operations. These companies include BYD, SAIC Motor, LY iTECH, BOZHON, Wolong, PIA,, Dafeng, Longcheer Technology, Lens, iSoftStone, and Luxshare ICT.
In December, the company announced the official production of its 5,000th humanoid robot, the general-purpose android “AGiBOT X2.” This milestone signifies that AGiBOT’s humanoid robot products have transitioned from small-batch trial production to stable mass production and large-scale delivery. Information disclosed at the same time indicates that by the end of 2025, the company’s total shipments exceeded 5,000 units.
Regarding business model exploration, AGiBOT participated in promoting the launch of the robot rental platform “BOTSHARE” in December. The platform, hosted by BOTSHARE (Shanghai) Technology Co., Ltd., with AGiBOT as a key participant, aims to lower the barrier to entry for humanoid robots through leasing, expanding application paths for enterprise and industry clients.
Unitree
In 2025, Unitree, previously known for its quadruped robots, further solidified its position in large-scale delivery and industry influence of humanoid robots.
During the Spring Festival, the company’s humanoid robots appeared on the 2025 CCTV Spring Festival Gala, achieving high-exposure on a national stage. This event significantly increased public awareness of humanoid robots, making Unitree one of the few robot companies widely recognized both in industry and among the general public.

In June 2025, Unitree completed its Series C financing, raising nearly 700 million yuan, with a post-investment valuation of approximately 12 billion yuan. This round of financing involved multiple industry and internet-backed institutions, and the funds will primarily be used to expand humanoid robot production capacity, strengthen core technology R&D, and support global market expansion.
Following the financing, Unitree’s actions in the capital market became more clearly defined. In July 2025, Unitree completed its IPO preparatory filing, with CITIC Securities serving as its advisor, officially entering the listing preparation stage.
In the following months, the company adjusted its listing structure, changing its name from “Hangzhou Unitree Robotics Co., Ltd.” to “Unitree Robotics Co., Ltd.” in October, in preparation for subsequent application. Entering the fourth quarter, Unitree continued to complete its full-size humanoid robot product line.
On November 10, it completed its IPO preparatory work. On November 15, its status on China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) website was updated to “preparatory work completed,” allowing it to submit its application materials. This was seen by outsiders as a crucial milestone in its quest to become the first A-share listed humanoid robot company.
On the product side, Unitree continued to expand its humanoid product line. On July 25, Unitree released its new bipedal humanoid robot, the R1, with a starting price of 39,900 yuan, significantly lowering the price range for humanoid robots. On October 20, the company released the upgraded Unitree H2, a general-purpose humanoid robot in the H series. On November 13, Unitree released a wheeled humanoid robot called G1-D for data collection.

On the business side, the company’s sales data released this year shows that the actual shipment volume of humanoid robots in 2025 exceeded 5,500 units, and the total number of mass-produced units exceeded 6,500 units. This only includes pure humanoid robots and does not include other models such as dual-arm wheeled robots.
Deep Robotics
In 2025, Deep Robotics further transferred its years of experience in complex environment robots to the humanoid robot field, focusing on solving the problem of long-term operation in real-world scenarios.
At the beginning of the year, Deep Robotics continued to advance the engineering verification of its humanoid robot platform based on its existing technology system. The company conducted multiple iterations of its previously launched humanoid robot DR01, focusing on improving overall reliability, environmental adaptability, and continuous operation stability.
In July, Deep Robotics completed a financing round of nearly 500 million yuan. This round of financing was led by institutions such as Fortune Capital and CHRC Fund, with participation from multiple industrial and state-owned capital investors.
On the product front, Deep Robotics was reaching a crucial juncture in the second half of the year. In October, the company released the industry-grade all-weather humanoid robot DR02. Positioned for engineering and industry applications, this product boasts an IP66 protection rating and can operate continuously in a wide temperature range from -20℃ to 55℃, designed for demanding scenarios such as power, emergency response, and security.

Along with the release of DR02, Deep Robotics was simultaneously advancing the verification of its embodied intelligent system in real-world scenarios. The robot began performing specific tasks such as inspection and monitoring in multiple industry settings to assess the system’s reliability and maintenance costs under long-term operating conditions.
Towards the end of the year, Deep Robotics was accelerating its capital investment again. In December, the company completed a Series C financing round of over 500 million yuan, led by institutions such as CMB International and China Asset Management, with strategic investment from funds related to China Telecom and China Unicom. This round of financing will primarily be used to expand the production capacity of humanoid and quadruped robots, strengthen core algorithms and systems engineering capabilities, and support larger-scale industry deployments.
Following this, Deep Robotics initiated IPO preparation and filing in late December, and subsequently completed a pre-IPO financing round led by a national-level industrial fund. Thus, the company completed multiple key financing rounds within a year and officially entered the listing preparation stage.
GALAXEA AI
In 2025, GALAXEA AI entered a critical period of simultaneous development of its product system and capital structure.
At the beginning of the year, GALAXEA AI took a significant step forward at the product level. In January, the company released the R1 series embodied robot platform, including multiple versions such as R1, R1 Pro, and R1 Lite, to support its “one brain, multiple forms” technical roadmap. This series of embodied robots served both as application carriers and played a crucial role in data collection and model training, becoming the foundational hardware platform for GALAXEA AI’s subsequent model and scenario development.

In February, GALAXEA AI completed a nearly 300 million yuan Series A financing round, led by Ant Group, with several existing shareholders continuing to invest. This round of financing will primarily be used to advance the R&D of embodied intelligence core technologies, iterate on its ontology products, and build its data system.
Subsequently, the company completed its A2/A3 rounds of financing in 2025, bringing the total size of its Series A financing to approximately $100 million, maintaining continuous capital supply throughout the year.
Technologically, GALAXEA AI reached a key milestone in the second half of the year. In August, the company released the end-to-end dual-system embodied intelligence model G0, as its core foundational model, used to uniformly handle perception, understanding, and action decision-making tasks. The release of G0 marks a significant milestone for GALAXEA AI in achieving a closed loop of “model-ontology-data,” providing a unified intelligent foundation for its subsequent cross-scenario generalization and large-scale training.
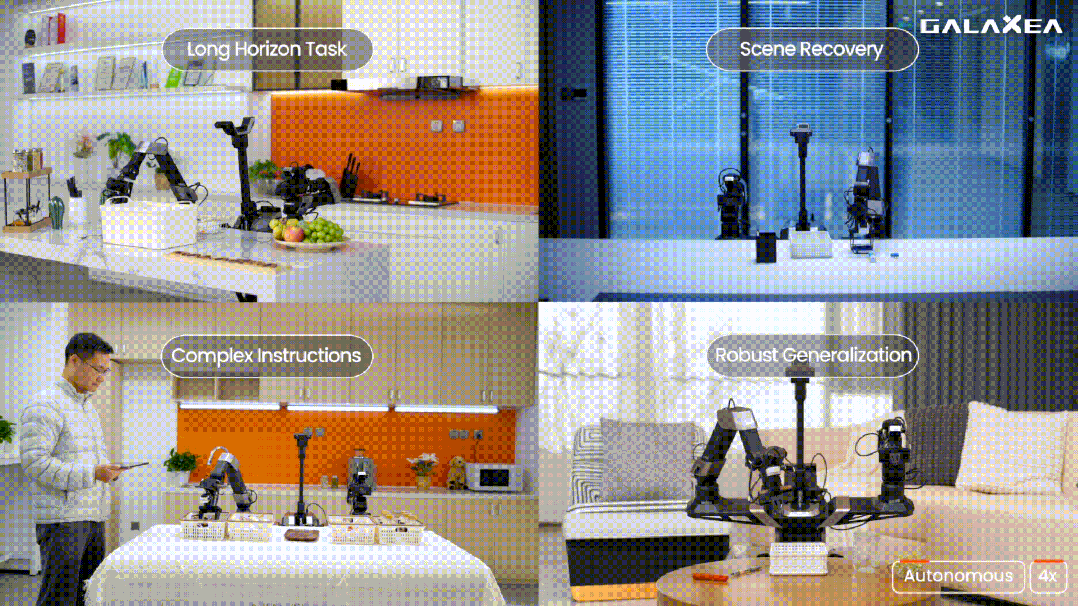

With the model and ontology system gradually becoming clearer, GALAXEA AI was beginning to show clearer signals on the commercialization side. In the second half of 2025, its wheeled dual-arm robot platform entered the large-scale deployment stage, receiving batch application feedback from customers in industries such as automotive and logistics. Multiple media outlets reported at the end of the year that GALAXEA AI had secured orders or letters of intent for thousands of units from leading companies, marking a significant milestone in its commercialization progress towards 2025.
ENGINE AI
In 2025, ENGINE AI’ path forward in the humanoid robot field was relatively clear, focusing on mass production, pricing, and order fulfillment.
At the beginning of the year, ENGINE AI began laying the groundwork for mass production and financing. The company announced the official mass production and launch of its humanoid robot PM01, available for sale on JD.com’s self-operated platform, priced at 188,000 yuan. It also launched the bipedal robot SA01, priced at 42,000 yuan.

Entering the second quarter, capital investment accelerated simultaneously. In April, ENGINE AI completed its Pre-A round of financing, led by Middle Eastern-backed Stone Venture, providing financial support for subsequent mass production and channel expansion.
In July, the company further announced the completion of its Pre-A++ and A1 rounds of financing, totaling nearly 1 billion yuan. The company secured funding from Rockets Capital in its Pre-A++ round and JD.com led the A1 round, with participation from CATL Capital and other institutions. The funds will primarily be used to expand production capacity, improve the product portfolio, and support order delivery capabilities.
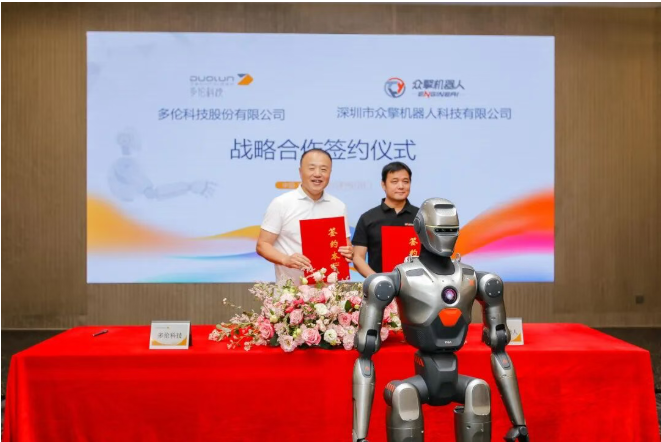
With the progress of financing, orders saw a clear upward trend in the third quarter. In September, ENGINE AI signed a strategic cooperation agreement with Duolun Technology, planning to purchase no fewer than 2,000 humanoid robots from ENGINE AI over the next three years for use in scenarios such as vehicle management offices and traffic safety experience centers. Information disclosed at the same time showed that ENGINE AI had set a production target of 500 humanoid robots per month, beginning preparations for large-scale delivery.

On the application level, ENGINE AI reached a deep strategic cooperation agreement with Sunpina in October, focusing on data collection and application verification of humanoid robots in home and commercial spaces, further expanding its application path in service and commercial scenarios.
In December, the company released the full-size humanoid robot T800 and launched large-scale sales, with a starting price of approximately 180,000 yuan. It also launched several configuration versions, including a basic version, an open-source version, Pro, and Max.

Concurrently with the new product launch, ENGINE AI completed its A1+ and A2 rounds of financing, led by Huangpu River Capital, Henan Investment Group Huirong Fund, and T-CAPITAL, and introduced several industrial and state-owned investors to provide further financial support for the mass production and delivery of the T800.
X Square Robot
2025 was a year of transition for X Square Robot, moving from end-to-end embodied intelligence basic model development to collaborative software and hardware development and intensive capital support.
At the beginning of the year, X Square Robot completed its Series A financing, led by Meituan Strategic Investment and with participation from institutions such as DragonBall Capital, providing a financial foundation for product and data capability advancement throughout the year. Subsequently, the company’s R&D team continued to iterate on its unified end-to-end general embodied intelligence model, aiming to build a fundamental intelligent layer capable of understanding perception, decision-making, and manipulation in the real physical world.
The WALL-A series of technical architectures proposed internally by the company became its core R&D direction in 2025, used to achieve joint reasoning and action decision-making capabilities based on vision-language-action (VLA), and to improve zero-shot generalization and long-tail task processing capabilities through a world model mechanism, which laid the foundation for the subsequent release of its large-scale model in 2025.
Parallel with model development, X Square Robot gradually advanced the practical verification of software and hardware synergy in 2025. While observing industry development trends, the company launched its first wheeled dual-arm “Quantum 2” robot platform in 2025 based on its self-developed WALL-A architecture, to verify the adaptability and execution capabilities of the general embodied model in specific physical tasks.

In September, X Square Robot announced the completion of its Series A+ financing round, led by Alibaba Cloud, with participation from CAS Investment, China Development Bank Capital, Sequoia Capital China, and others. This round of financing, totaling nearly 1 billion yuan, signifies further recognition from investors of its embodied intelligent basic model approach.
Also in September, X Square Robot further opened up its “basic model approach” to the industry: open-sourcing models and related capabilities such as WALL-OSS, attempting to establish a general capability foundation through open source and attract a developer ecosystem, which was one of its key actions in technology dissemination and ecosystem development in 2025.
Conclusion
Looking back at 2025, the development of Chinese humanoid robot unicorns worth billions of yuan has not shown a single development paradigm. Different companies show significant differentiation in technology choices, product forms, and commercialization paths, but the overall pace exhibits several common characteristics.
On the one hand, mass production and delivery have become key words. Whether it’s Unitree’ humanoid robots reaching the thousand-unit shipment level, GALBOT and ENGINE AI’s progress in orders and large-scale deployment, or AGiBOT’s layout around mass production systems and industrial collaboration, companies are generally shifting their focus from “can we make it?” to “can we deliver continuously?”.
On the other hand, capital remains intensive, but its purpose is more clearly defined. Many companies completed multiple rounds of financing in 2025, with funds being invested more in capacity expansion, engineering capabilities, and scenario implementation, rather than solely in single-point technological breakthroughs. Some companies are simultaneously pursuing IPO preparation or equity structure adjustments, making their capital paths clearer.
There is no single answer regarding technological routes. Some choose to rapidly scale up at low prices, some insist on engineering-grade reliability, some focus on basic models and ecosystems, and some build industrial networks through investment and joint ventures. This difference has not weakened the overall progress of the industry; on the contrary, it has allowed humanoid robots to advance simultaneously in different scenarios such as industry, service, and emergency response.
Overall, 2025 is more like a “year of differentiation” for China’s billion-dollar humanoid robot unicorns: their directions differ, but all are attempting to cross the threshold from prototype to the real world.




探索者论坛-scaled.jpg)
